Tacrolimus Neurotoxicity Risk Assessment Tool
Understanding Your Risk
This tool helps you assess your risk of tacrolimus neurotoxicity based on your symptoms and patient factors. It is not a substitute for medical advice.
When you’ve just had a transplant, the last thing you want is to feel like your body is turning against you. You’re taking tacrolimus to keep your new organ alive, but suddenly your hands won’t stop shaking. Your head pounds like it’s being squeezed in a vice. You can’t sleep. You feel foggy. And your doctor says your blood level is ‘in range.’ So why do you feel so awful?
Tremor Isn’t Just a Nuisance - It’s a Red Flag
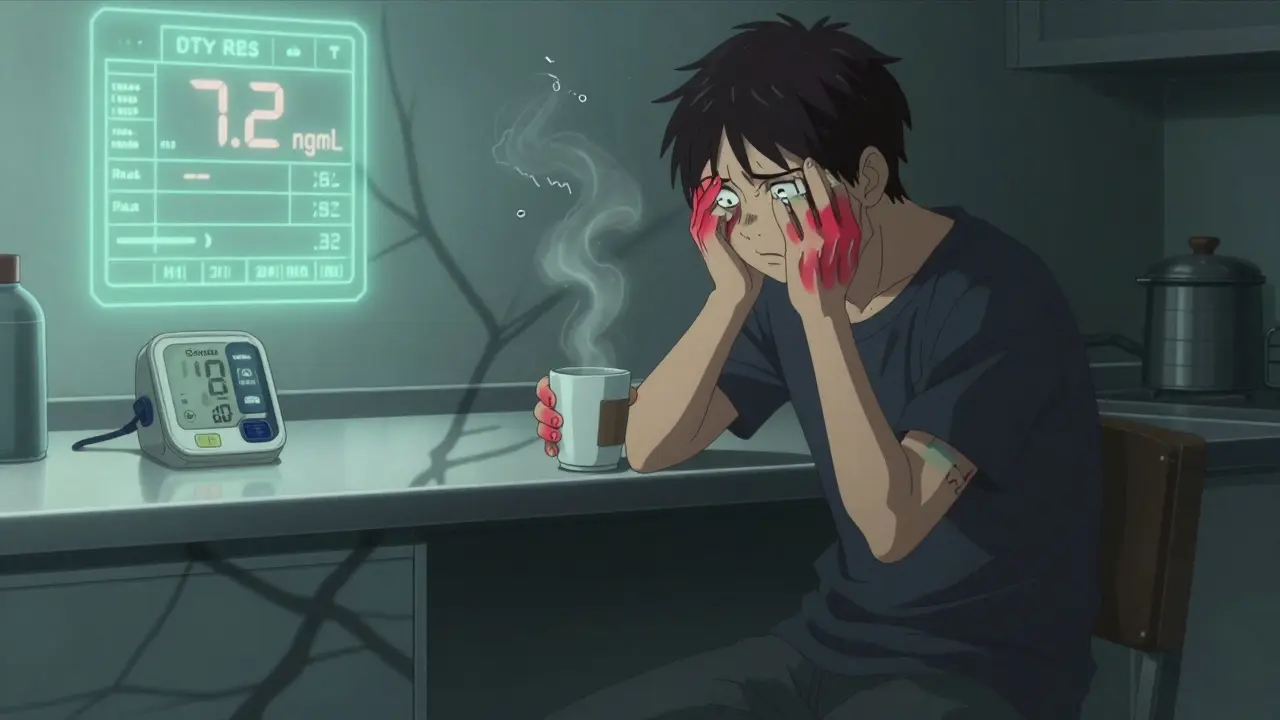
Tremor is the most common sign of tacrolimus neurotoxicity. In fact, about 65 to 75% of people who experience neurological side effects from tacrolimus report shaking hands or fingers. It’s not mild jitteriness. It’s the kind of tremor that makes it impossible to hold a coffee cup, button a shirt, or write your name clearly. And here’s the kicker: it often happens even when blood levels are perfectly within the therapeutic range of 5-15 ng/mL. A patient named ‘KidneyWarrior42’ on the American Transplant Foundation forum described it perfectly: “My tremor started at week 3 post-transplant when my tacrolimus level was 7.2 ng/mL - my neurologist said it was definitely tacrolimus even though it was in range.” That’s not rare. It’s common. The tremor isn’t random. It’s tied to how tacrolimus crosses the blood-brain barrier and interferes with nerve signaling. Some people are just more sensitive - and we’re starting to understand why. Genetics play a big role. If you have the CYP3A5*1 allele, your body breaks down tacrolimus faster, which means you need higher doses to stay protected from rejection. But higher doses mean more drug gets into your brain. That’s why some patients on ‘normal’ doses still get tremors, while others on higher doses don’t.Headache That Won’t Quit
Headache is the second most frequent symptom, hitting 45-55% of people with neurotoxicity. It’s not your typical tension headache. These are often described as constant, crushing, or throbbing. They don’t respond to ibuprofen or acetaminophen. Patients on Reddit’s r/transplant forum call them ‘tacrolimus headaches’ - a term that’s become unofficial medical slang. One user, ‘LiverSurvivor,’ wrote: “The headaches were constant and crushing - even at therapeutic levels of 6-8 ng/mL, nothing helped except when they switched me to cyclosporine.” That’s not an isolated case. Studies show that switching from tacrolimus to cyclosporine resolves headaches in over 70% of patients who don’t respond to dose reduction. What makes this so frustrating is that doctors often dismiss it as stress or dehydration. But when a headache starts within days of starting or increasing tacrolimus - especially if it’s new, severe, and unresponsive to usual treatments - it’s a red flag. It’s not just a side effect. It’s your brain telling you the drug is affecting it.What Are the Right Blood Levels? (And Why ‘In Range’ Isn’t Enough)
Most transplant centers aim for tacrolimus levels between 5-15 ng/mL, depending on the organ. Kidney recipients usually target 7-10 ng/mL early on, then drop to 5-8 ng/mL after three months. Liver recipients often start higher - 8-12 ng/mL - then taper to 5-10 ng/mL. Heart and lung recipients fall in the same 5-10 ng/mL range. But here’s the problem: tacrolimus neurotoxicity doesn’t always follow the numbers. A 2023 study in Annals of Transplantation found no significant difference in average blood levels between patients who developed neurotoxicity and those who didn’t. That means two people with identical levels can have wildly different experiences. One feels fine. The other can’t walk straight. Why? Because blood levels don’t tell you what’s happening in the brain. The blood-brain barrier isn’t the same for everyone. Some people have leakier barriers due to inflammation, infection, or genetics. Others have more of the transport proteins that shuttle tacrolimus into brain cells. That’s why some patients develop symptoms at 6 ng/mL, while others tolerate 18 ng/mL without issue. Even the guidelines admit this. The 2022 KDIGO guidelines say therapeutic ranges are just starting points - not guarantees of safety. The real goal isn’t just to stay in range. It’s to stay symptom-free in range.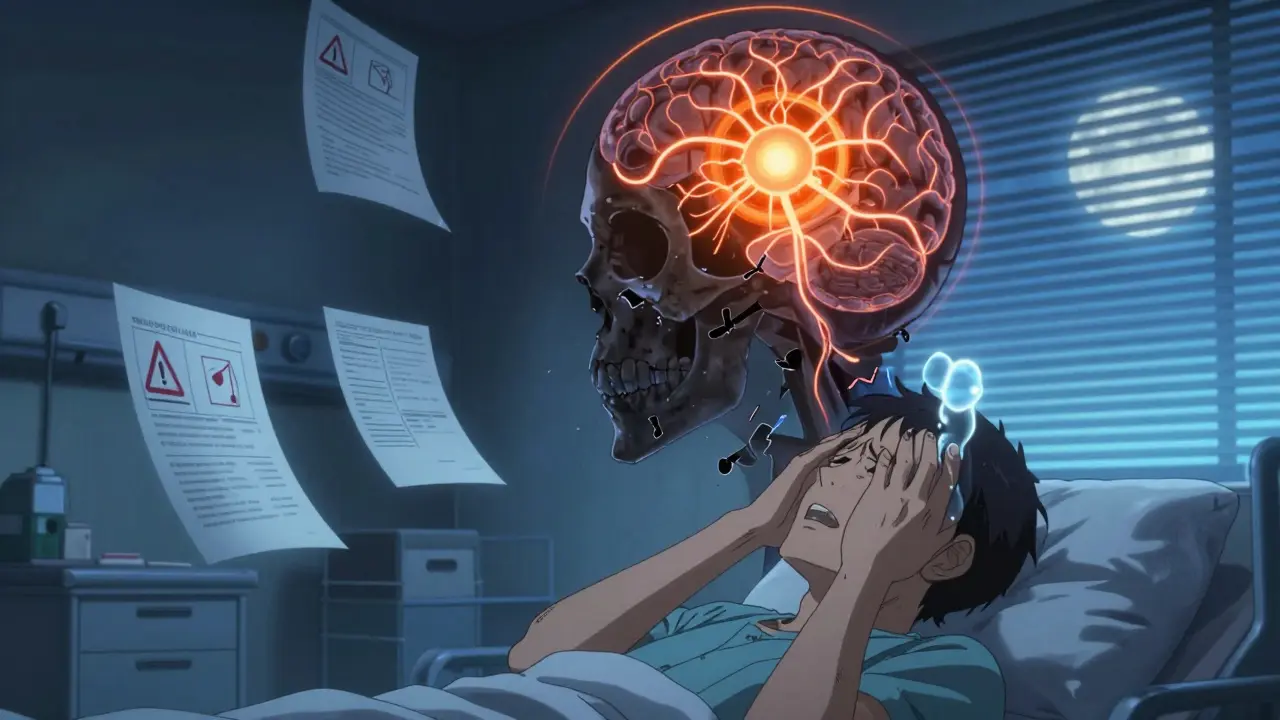
Who’s at Highest Risk?
Not everyone gets neurotoxicity. But some groups are far more vulnerable. Liver transplant recipients are hit hardest - 35.7% develop symptoms, compared to 22.4% for kidney, 18.9% for lung, and 15.2% for heart. Why? It’s not fully understood, but liver patients often have higher tacrolimus doses early on, and their livers are still healing, which can alter how the drug is metabolized. Age matters too. Older patients (over 60) are more likely to develop tremor and confusion. So are people with pre-existing neurological conditions, like migraines or epilepsy. And electrolyte imbalances - especially low sodium (hyponatremia) - double the risk. One study showed correcting sodium levels alone resolved mild neurotoxicity in 28% of cases, without touching the tacrolimus dose. And then there are drug interactions. If you’re on antibiotics like linezolid, antifungals like fluconazole, or even sedatives like midazolam or propofol, your risk spikes. These drugs slow down how your body clears tacrolimus, causing levels to creep up - even if you haven’t changed your dose.When It Gets Serious: PRES, Encephalopathy, and CIDP
Most neurotoxicity is mild: tremor, headache, insomnia. But in 1-3% of cases, it turns dangerous. Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome (PRES) is the scariest. It causes swelling in the back of the brain, leading to seizures, vision loss, confusion, or even coma. MRI scans show bright spots in the occipital lobes. It’s reversible - if caught early. But if missed, it can lead to permanent damage or death. Less common but equally serious is Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyradiculoneuropathy (CIDP), which causes progressive weakness, numbness, and loss of reflexes. It’s rare - only 0.5-1.5% of tacrolimus users - but it mimics multiple sclerosis and is often misdiagnosed. And then there’s central pontine myelinolysis - a rare but devastating condition where the brainstem’s protective coating gets stripped away. Autopsy studies show it happens in up to 17% of liver transplant patients who had severe electrolyte shifts. It’s often fatal. These aren’t theoretical risks. They’re documented in case reports, hospital records, and FDA databases. And they’re why you can’t ignore a new tremor or headache - even if your blood level looks fine.
What Do You Do If You Have Symptoms?
Step one: Don’t panic. But don’t wait either. If you’re experiencing tremor, headache, confusion, or vision changes after starting tacrolimus, tell your transplant team immediately. Don’t wait for your next blood test. Don’t assume it’s ‘just stress.’ Here’s what usually happens next:- Dose reduction: The first step is often lowering the dose by 10-20%. Many patients see improvement within 3-7 days. One patient on the National Kidney Foundation forum reported complete tremor resolution within 72 hours after dropping from 0.1 mg/kg to 0.07 mg/kg.
- Switching drugs: If symptoms persist, switching to cyclosporine is common. It’s less effective at preventing rejection - about 20-30% higher risk - but it causes neurotoxicity in only 15-20% of patients. For many, the trade-off is worth it.
- Correcting electrolytes: If your sodium is low, fixing that alone can help. Magnesium and potassium imbalances also contribute.
- Stopping interacting drugs: If you’re on linezolid, fluconazole, or a sedative, your team may switch you to a safer alternative.



12 Comments
Daniel Pate
January 12, 2026 AT 12:04Tacrolimus neurotoxicity isn't just about blood levels-it's about how your brain interprets the drug. I've seen patients with levels at 14 ng/mL feel fine while others crash at 6. Genetics, inflammation, even gut microbiome differences play a role. We're treating a system, not a number.
Amanda Eichstaedt
January 14, 2026 AT 02:39I was that patient who couldn't hold a coffee cup at week 4 post-liver transplant. Level was 7.8. Doctor said 'it's normal.' I cried in the parking lot. Three weeks later, they switched me to cyclosporine and I slept for the first time in months. Your symptoms are valid. Push harder.
Jose Mecanico
January 14, 2026 AT 20:36Interesting point about CYP3A5. My cousin got tested before his transplant and they adjusted his dose upfront. No tremors. No headaches. Just quiet recovery. Maybe we need to make genetic screening standard, not optional.
Alex Fortwengler
January 16, 2026 AT 00:43Of course your head hurts. You're on a poison that was designed to shut down your immune system. The fact that you're still alive means your body's fighting a war on three fronts. Stop expecting to feel normal. This isn't a side effect-it's a ceasefire with death. You're lucky you're not dead.
Eileen Reilly
January 17, 2026 AT 16:46okay but like… why do doctors always act like you're being dramatic when you say your head feels like its being crushed by a hydraulic press? i had a 10/10 headache for 11 days and they gave me tylenol. i swear to god if i hadnt screamed at the nurse i woulda had a seizure and theyd have blamed it on stress. also my sodium was 128 and no one checked until i demanded it. this is medical gaslighting 101
Cecelia Alta
January 18, 2026 AT 21:13Let me tell you about my sister. She got a kidney transplant, started tacrolimus, and within days her hands shook so bad she dropped her phone into the toilet. Then she got a migraine that lasted 17 days. They told her it was anxiety. She went to three different neurologists before one said, 'This is tacrolimus.' They lowered her dose and she cried because she could finally hold a pen again. And now? They're talking about switching her to a new drug that doesn't turn your brain into a glitchy video game. But it's not even approved yet. So she's stuck. And so are we. This isn't medicine. It's a gamble with your sanity.
steve ker
January 20, 2026 AT 13:29levels mean nothing brain dont care what lab says you feel bad you need new drug
laura manning
January 20, 2026 AT 19:46It is imperative to underscore that the prevailing clinical paradigm, predicated upon therapeutic drug monitoring via serum concentrations, remains fundamentally inadequate in predicting neurotoxic sequelae. The pharmacokinetic variability engendered by polymorphic CYP3A5 expression, coupled with interindividual differences in blood-brain barrier permeability, renders serum levels a statistically non-predictive metric. Consequently, symptom-based titration-not numerical targets-must constitute the cornerstone of clinical decision-making.
Katherine Carlock
January 21, 2026 AT 10:08I just want to say thank you for writing this. I was scared to speak up because I thought I was just being weak. But reading this made me realize I’m not crazy. My tremor wasn’t ‘nerves.’ My headache wasn’t ‘stress.’ I’m not overreacting. I’m surviving.
Sona Chandra
January 21, 2026 AT 15:25So what? You got a headache. Millions of people get headaches. You think you’re special because you’re on immunosuppressants? Try living with cancer. Try being poor and not even getting the drug. Stop whining. Your life was saved. Be grateful.
Jennifer Phelps
January 21, 2026 AT 23:26Anyone else notice how often PRES is missed because doctors think it’s a stroke? I saw a case where the MRI was done 3 days late because they thought it was a migraine. By then the swelling had spread. They saved her but she lost peripheral vision. We need better awareness
Craig Wright
January 22, 2026 AT 13:31In the United Kingdom, we have adopted a more structured approach to tacrolimus management, with mandatory CYP3A5 genotyping in all high-risk recipients since 2021. The reduction in neurotoxicity-related admissions has been statistically significant. The American system’s reliance on reactive, rather than preemptive, medicine is frankly archaic. We must align our protocols with evidence-not tradition.