Introduction to Atrial Fibrillation and Atrial Flutter
When it comes to irregular heart rhythms, two conditions that often come to mind are atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter. While both of these conditions can affect the functioning of the heart, they are not the same thing. In this article, we will delve into the differences between atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter, as well as their causes, symptoms, and treatment options.
Understanding the Heart's Electrical System
To better understand the differences between atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter, it's important to first learn about the heart's electrical system. The heart is a complex organ that relies on a coordinated electrical system to function properly. This system controls the rate and rhythm of the heartbeats, ensuring that blood is pumped efficiently throughout the body.
When the electrical signals in the heart become disrupted, it can lead to irregular heart rhythms, or arrhythmias. Atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter are two common types of arrhythmias that affect the upper chambers of the heart, known as the atria.
Defining Atrial Fibrillation
Atrial fibrillation, often referred to as AFib, is the most common type of irregular heartbeat. It occurs when the electrical signals in the atria become chaotic and disorganized. This causes the atria to quiver or fibrillate, rather than contract normally. As a result, blood may pool in the atria, increasing the risk of blood clots and stroke.
AFib can be classified into several categories, including paroxysmal (intermittent), persistent, and permanent. The severity and duration of the episodes determine the classification and can impact the treatment options.
Defining Atrial Flutter
Atrial flutter, while less common than atrial fibrillation, is another type of irregular heartbeat that affects the atria. In atrial flutter, the electrical signals in the atria become disrupted, causing the atria to beat rapidly and inefficiently. This rapid beating can lead to a reduced blood flow to the rest of the body and an increased risk of blood clots and stroke.
Atrial flutter is often classified as either typical or atypical, depending on the specific pattern of the electrical signals in the heart. This distinction can influence the treatment approach for the condition.
Comparing the Symptoms of Atrial Fibrillation and Atrial Flutter
While both atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter can cause similar symptoms, there are some subtle differences between the two conditions. Common symptoms experienced by individuals with either condition may include heart palpitations, shortness of breath, fatigue, dizziness, and chest pain.
However, some people with atrial fibrillation may not experience any noticeable symptoms, while others with atrial flutter may describe their heart palpitations as more regular or organized. It's important to consult with a healthcare professional if you are experiencing any of these symptoms, as they can help determine the specific cause of your irregular heartbeat.
Causes and Risk Factors
There are several factors that can increase the risk of developing atrial fibrillation or atrial flutter. Some common risk factors for both conditions include age, high blood pressure, heart disease, obesity, and excessive alcohol consumption. Additionally, certain medical conditions, such as diabetes, sleep apnea, and thyroid disorders, can also increase the risk of these arrhythmias.
It's important to note that while atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter share many risk factors, they can also occur independently of one another. In some cases, atrial flutter can develop as a result of atrial fibrillation treatment, or vice versa.
Diagnosis and Testing
Diagnosing either atrial fibrillation or atrial flutter typically involves a thorough examination by a healthcare professional, as well as the use of specific tests such as an electrocardiogram (ECG) or a Holter monitor. These tests can help identify the specific type of irregular heartbeat, as well as any underlying conditions that may be contributing to the arrhythmia.
In some cases, additional tests, such as an echocardiogram or a stress test, may be recommended to further assess the health of the heart and determine the appropriate treatment plan.
Treatment Options for Atrial Fibrillation and Atrial Flutter
While the specific treatment approach for atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter may vary depending on the underlying cause and severity of the condition, there are some common treatment options that may be recommended for both conditions. These can include medications to control heart rate and rhythm, blood thinners to reduce the risk of blood clots and stroke, and lifestyle changes to address risk factors such as high blood pressure and obesity.
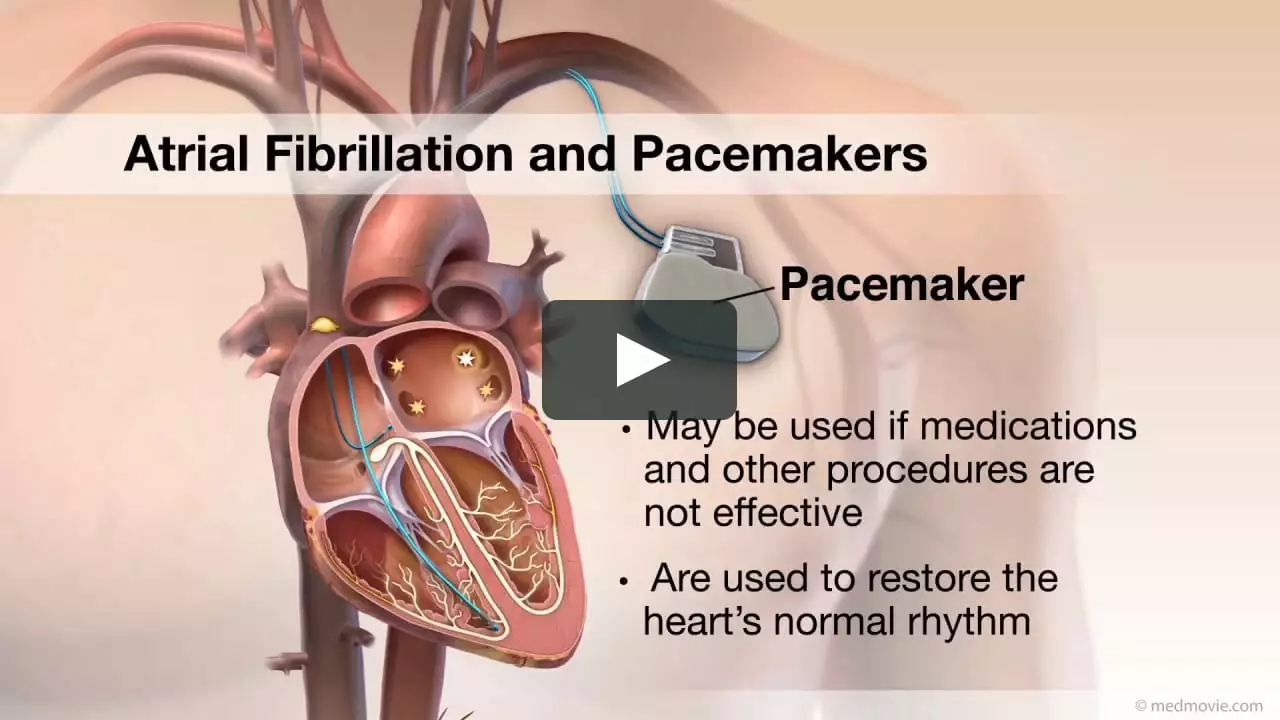
In some cases, more invasive treatments, such as electrical cardioversion, catheter ablation, or the implantation of a pacemaker or defibrillator, may be necessary to manage the irregular heartbeat effectively.
Conclusion
While atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter share many similarities, it's important to understand the differences between these two arrhythmias. By recognizing the distinct characteristics of each condition, healthcare professionals can provide more accurate diagnoses and tailored treatment plans for their patients. If you suspect you may have an irregular heartbeat, it's crucial to seek medical attention promptly to ensure the best possible outcomes for your heart health.


18 Comments
S Love
May 18, 2023 AT 10:25Atrial fibrillation is such a sneaky one-sometimes you feel it, sometimes you don’t. I had a friend who thought he was just stressed until his ECG showed he was in AFib for weeks. Scary stuff.
Pritesh Mehta
May 18, 2023 AT 21:13Let us not forget that in the grand metaphysical architecture of cardiac electrophysiology, the atrial flutter is not merely a rhythm-it is a metaphysical assertion of order against the chaotic entropy of fibrillation. Western medicine, in its reductionist obsession with pharmacological intervention, fails to recognize that flutter is the soul’s disciplined heartbeat, whereas fibrillation is the body’s existential scream.
India, with its millennia-old Ayurvedic traditions, has always understood that rhythm is sacred. The Vedic sages spoke of prana as the conductor of cardiac harmony-modern cardiologists, armed with their ECGs and ablation catheters, are but children playing with fire in the temple of the heart.
Why do we treat symptoms when we could restore cosmic balance? Why do we prescribe anticoagulants when we could prescribe pranayama? The answer, of course, lies in the colonial indoctrination of medical education-where the West stole the knowledge of the East and repackaged it as ‘science’.
And yet, we still cling to the illusion that a catheter can fix what the soul has unraveled. The flutter, with its beautiful, predictable sawtooth pattern, is nature’s poetry. The fibrillation? A broken symphony. Who are we to silence the former with ablation?
Perhaps the real question is not how to treat these arrhythmias, but why we have allowed our lives to become so dissonant that our hearts must rebel in such dramatic fashion.
Modern life-processed food, screen addiction, chronic stress-is the true arrhythmia. The heart is merely reflecting the chaos we’ve cultivated.
And so, I ask you: if your heart is fluttering, is it not trying to tell you to slow down? To breathe? To return to the rhythm of the earth?
Western medicine offers pills. Ancient wisdom offers presence.
Which will you choose?
Billy Tiger
May 19, 2023 AT 05:15AFib is just a fancy way of saying your heart’s glitching like a bad wifi connection. Flutter’s at least got a pattern. If you’re not on blood thinners you’re asking for a stroke. End of story.
Katie Ring
May 21, 2023 AT 03:47It’s fascinating how both conditions are essentially the heart’s version of mental burnout-too much stress, too little rest. We treat the rhythm, but we never treat the life that caused it. Maybe that’s the real cure.
Adarsha Foundation
May 21, 2023 AT 11:13I appreciate how this article clearly distinguishes the two without sensationalizing. As someone from India, I’ve seen many patients confused between these two, especially when they hear ‘irregular heartbeat’ from a local doctor. Clear explanations like this help bridge that gap.
Alex Sherman
May 22, 2023 AT 05:33Of course the article mentions ablation and cardioversion like they’re miracle cures. Meanwhile, the real cause-chronic inflammation from processed food, sugar, and sedentary lifestyles-is ignored. We’ve turned the heart into a machine that needs parts replaced instead of a living organ that needs care.
Oliver Myers
May 23, 2023 AT 18:53Wow, this was so well-written and easy to understand! I’ve been dealing with AFib for a few years now and I still get confused between flutter and fibrillation-this cleared it up for me in a way my cardiologist never did. Thank you for breaking it down without jargon! 🙏❤️
John Concepcion
May 24, 2023 AT 17:23So you’re telling me after 20 years of medical school they still can’t tell the difference between a flutter and a fibrillation? LOL. Just stick a catheter in there and call it a day. You people are ridiculous.
Caitlin Stewart
May 26, 2023 AT 08:39I never realized how much emotional stress affects rhythm until I had my first episode. My doctor said it was ‘idiopathic’-but I knew it was the divorce, the job loss, the sleepless nights. The heart doesn’t lie. It just speaks in a language we ignore until it screams.
Emmalee Amthor
May 27, 2023 AT 18:24So if flutter is organized and fib is chaos… then maybe we’re just too stressed out to have a calm heart? Like our whole life is one big AFib episode? Hmm. Maybe we need to stop trying to fix the heart and start fixing our lives. Just a thought.
Leslie Schnack
May 28, 2023 AT 06:14Does anyone know if atrial flutter can turn into AFib over time? I’ve read conflicting things. My dad had flutter for years and now he’s in permanent AFib-was that inevitable?
Saumyata Tiwari
May 28, 2023 AT 23:07Western medicine continues to profit from chronic arrhythmias. In India, we have yoga, pranayama, and fasting-tools that reset the autonomic nervous system without drugs. Yet we are told to swallow pills and get ablated. The system is broken, and you are its loyal servant.
Roy Scorer
May 30, 2023 AT 06:41People think AFib is just ‘a little irregular heartbeat.’ No. It’s a silent killer. And you know who gets ignored? The ones who don’t have symptoms. The asymptomatic. The ones who think they’re fine until they collapse. You think you’re healthy? You’re not. You’re just lucky.
Marcia Facundo
May 30, 2023 AT 11:23My mom had flutter. They did the ablation. It worked for two years. Then AFib came back. Now she’s on warfarin and hates it. I just wish they’d told us earlier that lifestyle changes matter more than the catheter.
Ajay Kumar
May 30, 2023 AT 15:06Everyone says flutter is better than AFib but that’s just because it’s easier to treat. What if the real problem is that the heart is trying to tell us something? What if we’re not supposed to ‘fix’ it but listen to it? What if the rhythm is trying to slow us down because we’re moving too fast? You think your job matters more than your heart? Think again.
And don’t even get me started on how big pharma markets ablation like it’s a spa day. It’s not. It’s a burn. A burn on your heart tissue. And they call it ‘cure’? Please.
And what about the people who get it after surgery? Or after a virus? Or after a breakup? We don’t ask those questions. We just zap it and move on.
We treat the symptom, not the soul.
And that’s why it keeps coming back.
Joseph Kiser
May 31, 2023 AT 14:11My brother got AFib after a hiking trip in the Rockies. He was fit, ate clean, no caffeine. Turns out it was a viral myocarditis. No one talks about that. Stress, yes. But viruses? Genetics? Autoimmune? Those are the real culprits. We need more research-not just more ablations. ❤️🫀
Hazel Wolstenholme
May 31, 2023 AT 16:18It’s amusing how we anthropomorphize cardiac rhythms-‘flutter’ sounds almost elegant, like a butterfly’s wing, while ‘fibrillation’ sounds like a malfunctioning toaster. Language shapes perception. We treat flutter as ‘less bad’ because it sounds less violent. But physiologically, both are equally dangerous. The nomenclature is a distraction.
And yet, we cling to it. Because to admit that both are equally terrifying would require us to confront mortality head-on. So we rename the terror. We call it ‘flutter’ and pretend it’s benign.
How quaint.
Mike Laska
May 31, 2023 AT 16:32I had flutter for 8 months. No symptoms. Just a random ECG during a physical. They said ‘it’s not dangerous.’ Then I got AFib after a bad breakup. That’s when I felt it. The palpitations. The dread. The exhaustion. I thought I was dying. Turns out I was just heartbroken. And my heart knew it before I did.
They gave me beta-blockers. I cried every night. I started therapy. I stopped checking my pulse. And guess what? The AFib faded. Not because of the meds. Because I finally stopped running from myself.
So yeah. It’s not just about the heart.
It’s about the soul.
And we’re all just trying to keep it beating.